什么是内网穿透?
内网穿透,指的是将局域网中的服务映射到公网,使外部用户可以访问到原本仅在内网中运行的服务。
例如:
- 调试本地 Web 项目;
- 外网访问家里的 NAS 或博客;
- 远程控制个人电脑等。
实现条件
- 一台拥有公网 IP 的服务器(云服务器);
- 内网中的客户端程序可以主动连接该云服务器。
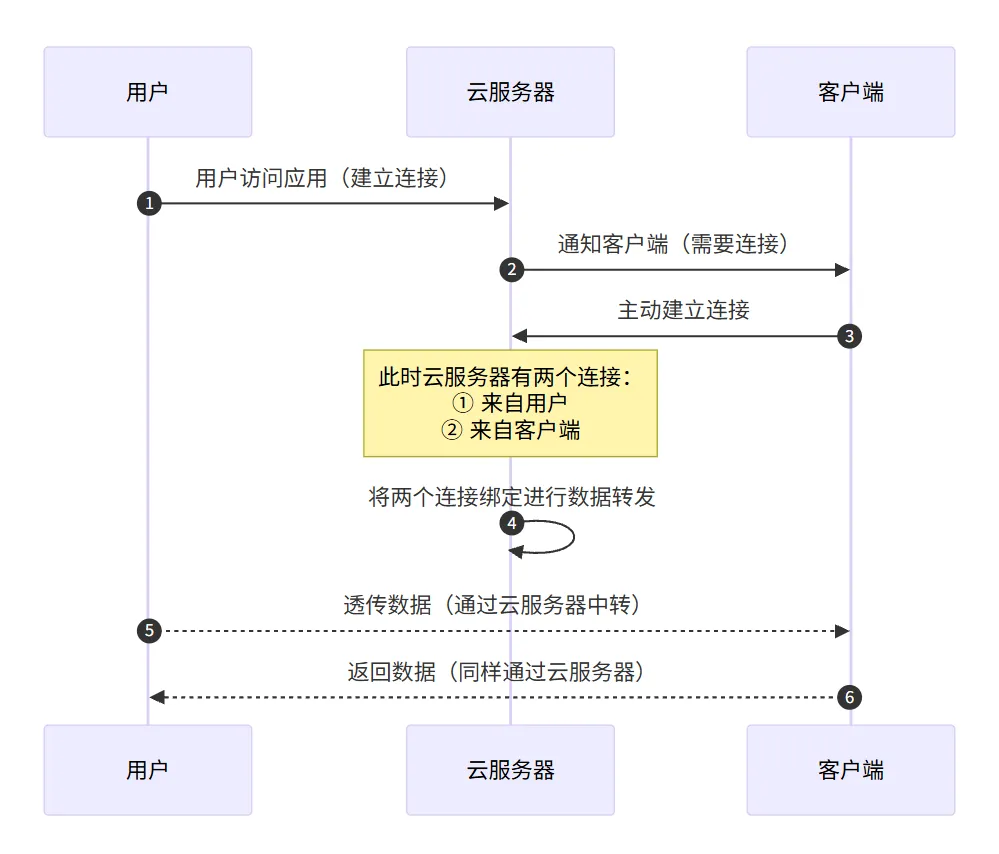
实现原理
整体流程如下:
1.用户访问应用会走云服务器,云服务器会告诉客户端(个人电脑)需要连接,赶快连接我。
2.客户端收到服务器的命令,马上连接云服务器。
3.这时候在云服务器有两个连接,一个是用户连接,另一个是客户端连接,让他们相互交换数据就行。
如图所示:
项目代码
下面是一个基于 Java AIO 的最小实现,使用虚拟线程简化了并发处理。
客户端代码(运行于内网)
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//虚拟线程池
var executor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor();
// 从系统属性获取值,若未设置则使用默认值
int appPort = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("appPort", "3389"));
int remotePort = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("remotePort", "8888"));
String remoteHost = System.getProperty("remoteHost", "192.168.1.195");
var client = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open();
Future<Void> connect = client.connect(new InetSocketAddress(remoteHost, remotePort));
//等待连接
connect.get();
System.out.printf("客户端连接成功:appPort:%d,remotePort:%d,remoteHost:%s%n",appPort,remotePort,remoteHost);
//写入100告诉服务端是用来交换数据的
var buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(4).putInt(100).flip();
var l = client.write(buffer).get();
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1);
//读取服务端
var len = client.read(buffer).get();
if(len < 0){
client.close();
}else{
//切换读
buffer.flip();
//服务端需要连接,提供连接
if (buffer.get() == 66) {
executor.submit(() -> {
try (
//连接远程
var remote = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open();
//连接本地
var local = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open();
) {
Future<Void> remoteConnect = remote.connect(new InetSocketAddress(remoteHost, remotePort));
Future<Void> localConnect = local.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", appPort));
localConnect.get(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
remoteConnect.get(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println(localConnect);
//告诉服务端是一个连接
var bf = ByteBuffer.allocate(4).putInt(200).flip();
remote.write(bf).get(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
//开始交换数据
Future<?> taskFuture1 = executor.submit(() -> {
transferData(remote, local);
});
Future<?> taskFuture2 = executor.submit(() -> {
transferData(local, remote);
});
taskFuture1.get();
taskFuture2.get();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
});
} else {
client.close();
break;
}
}
}
}
private static void transferData(AsynchronousSocketChannel srcChannel, AsynchronousSocketChannel dstChannel) {
int readLen;
do{
try {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Future<Integer> read1 = srcChannel.read(buffer);
readLen = read1.get();
if(readLen>0){
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.remaining()>0){
Future<Integer> write1 = dstChannel.write(buffer);
write1.get();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
break;
}
}while (readLen>0);
}
}
服务端代码(运行于云服务器)
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int port = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("port", "8888"));
//开启服务端
try(var serverChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open()){
serverChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress("0.0.0.0", port));
System.out.printf("服务端启动:%d%n",port);
//客户端连接,用来告知需要连接
AtomicReference<AsynchronousSocketChannel> client = new AtomicReference<>(null);
//客户端那边提供的连接队列
LinkedBlockingQueue<AsynchronousSocketChannel> channelQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
//虚拟线程池
var executor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor();
while (!Thread.interrupted()){
try {
AsynchronousSocketChannel srcChannel = serverChannel.accept().get();
System.out.println("有连接:"+srcChannel);
// 提交到虚拟线程池
executor.submit(() -> {
try {
var buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
var len = srcChannel.read(buffer).get();
//切换读状态
buffer.flip();
if(len < 0) {
srcChannel.close();
}else if(len == 4){
//用一个整形长度判断
var code = buffer.getInt();
if(code == 100){
//关闭旧连接
if(client.get() != null){
client.get().close();
}
//替换新客户端连接
client.set(srcChannel);
}else if (code == 200){
//加入连接队列
channelQueue.offer(srcChannel);
}else{
//错误数据关闭连接
srcChannel.close();
}
}else{
//告诉客户端需要连接
if(client.get() == null){
//没有客户端连接
srcChannel.close();
}else{
//告知客户端需要连接
client.get().write(ByteBuffer.wrap(new byte[]{66})).get();
AsynchronousSocketChannel asc = channelQueue.poll(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if(asc!=null){
try (asc;srcChannel){
while (buffer.remaining()>0){
asc.write(buffer).get();
}
System.out.println(srcChannel);
//开始交换数据
Future<?> taskFuture1 = executor.submit(() -> {
transferData(srcChannel, asc);
});
Future<?> taskFuture2 = executor.submit(() -> {
transferData(asc, srcChannel);
});
taskFuture1.get();
taskFuture2.get();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if(srcChannel!=null){
try {
srcChannel.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
private static void transferData(AsynchronousSocketChannel srcChannel, AsynchronousSocketChannel dstChannel) {
int readLen;
do{
try {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Future<Integer> read1 = srcChannel.read(buffer);
readLen = read1.get();
if(readLen>0){
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.remaining()>0){
Future<Integer> write1 = dstChannel.write(buffer);
write1.get();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
break;
}
}while (readLen>0);
}
}
小结
本文实现了一个简洁的内网穿透工具,主要依赖 Java 的 AIO 特性和虚拟线程机制,无需第三方库,便于理解和自定义扩展。